Glass Melting Production Process
See OHARA’s step-by-step process for melting optical glass here.
Technical Capabilities Glass Melting
Optical Business Strip Glass

Mixing Raw Materials
This process measures the raw materials for glass in grams and blends them. After measurement, the raw materials are uniformly stirred in a mixer, and then packed into bags and boxes to be carried to the next process.

Primary Melting
The mixture of raw materials prepared in the previous process is melted in a melting furnace at a high temperature, ranging from 1,000 to 1450 °C. This melt is then poured onto a tray-shaped platform to solidify before being crushed manually and by machines into small glass pieces called cullets, which are brought to the next process.

Mixing Cullet
An amount of cullets is weighed out to the specifications in the retrieval instructions, and then they are checked with a metal detector before going to the next process.

Secondary Melting/Strip Glass
The cullets measured out in the previous process are put into a melting furnace and melted at a high temperature. In this process, air bubbles and foreign substances are removed. After that, the melt is poured into a metal mold in which a glass plate is formed.
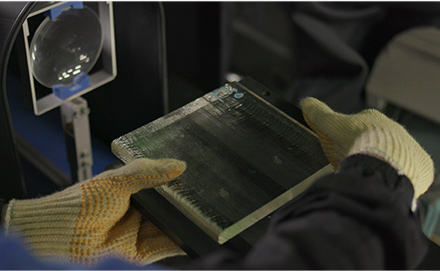
Material Inspection
This process examines products and test pieces. Test pieces that are approximately 15 cm long are taken at intervals of 5 meters. Testing machines check the quality of various aspects of the test pieces, such as the inclusion of any air bubbles, paying the utmost attention to prevent any nonconforming products from going out. Conforming products are cut and measured and then transported to the warehouse.

